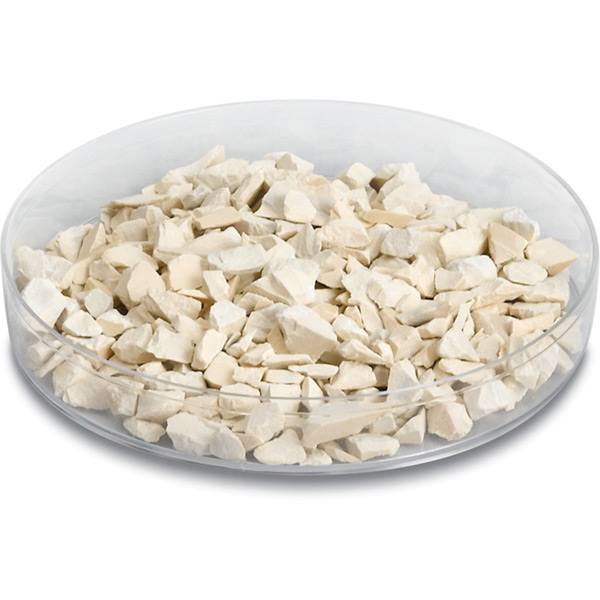
Titanium Dioxide (TiO2) White Pieces Overview
We sell these pellets and pieces by unit weight for evaporation use in deposition processes. These approximate materials prices are published to provide budgetary guidelines. Actual prices can vary and may be higher or lower, as determined by availability and market fluctuations. To speak to someone directly about current pricing, please click here .
Titanium Dioxide (TiO2) General Information
Titanium dioxide is a chemical compound with a chemical formula of TiO2. It is white in appearance with a density of 4.26 g/cc, a melting point of 1,830°C, and a vapor pressure of 10-4 Torr at ~1,300°C. The largest commercial application of titanium dioxide is as a white pigment for paint due to its brightness and high refractive index. It is also a principal ingredient in sunscreen because of its unique ability to absorb UV light. It is evaporated under vacuum primarily for reflective optical coatings and optical filters.
Titanium Dioxide (TiO2) Specifications
| Material Type | Titanium (IV) Oxide |
| Symbol | TiO2 |
| Color/Appearance | White-Beige, Gray-Black |
| Melting Point (°C) | 1,830 |
| Theoretical Density (g/cc) | 4.23 |
| Z Ratio | 0.4 |
| E-Beam | Fair |
| Thermal Evaporation Techniques |
Boat: W, Mo Basket: W |
| E-Beam Crucible Liner Material | FABMATE®, Tantalum |
| Temp. (°C) for Given Vap. Press. (Torr) | 10-4: ~1,300 |
| Comments | Suboxide, must be reoxidized to rutile. Ta reduces TiO2 to TiO and Ti. |
| Suggested QCM Crystal | Alloy Crystal: 750-1002-G10**** |
**** Suggestion based on previous experience but could vary by process. Contact local KJLC Sales Manager for further information
Empirical Determination of Z-Factor
Unfortunately, Z Factor and Shear Modulus are not readily available for many materials. In this case, the Z-Factor can also be determined empirically using the following method:
- Deposit material until Crystal Life is near 50%, or near the end of life, whichever is sooner.
- Place a new substrate adjacent to the used quartz sensor.
- Set QCM Density to the calibrated value; Tooling to 100%
- Zero thickness
- Deposit approximately 1000 to 5000 A of material on the substrate.
- Use a profilometer or interferometer to measure the actual substrate film thickness.
- Adjust the Z Factor of the instrument until the correct thickness reading is shown.
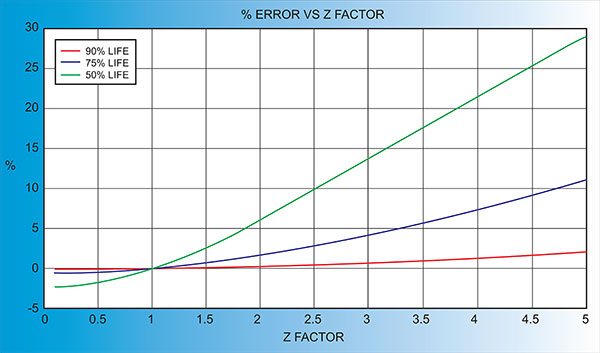
Another alternative is to change crystals frequently and ignore the error. The graph below shows the % Error in Rate/Thickness from using the wrong Z Factor. For a crystal with 90% life, the error is negligible for even large errors in the programmed versus actual Z Factor.
Thermal Evaporation of Titanium Dioxide (TiO2)
Titanium dioxide can be thermally evaporated from a tungsten or molybdenum boat. We would recommend our EVS8B005W or EVS8B005MO. Pressure should be monitored to ensure outgassing is at an acceptable level before increasing power. A partial pressure of O2 at 1-2 x 10-4 Torr is recommended. The evaporation temperature varies with composition. Titanium dioxide has a vapor pressure of 10-4 Torr at ~1,300°C. In our experience, we have been able to achieve a deposition rate of 3-5 angstroms per second.
KJLC offers white and black titanium dioxide pieces. The difference in color is due to the material's degree of oxidation. Fully oxidized titanium dioxide is white. With even a slight reduction in oxygen, the material becomes grey to black in color. When evaporating titanium dioxide it is necessary to melt the material before depositing films. Titanium has several stable oxides, and when the material is heated it reduces (evolves oxygen) and turns black. Regardless of which material is used (white or black), the material will turn black and evolve oxygen as it is heated. Once outgassing subsides, the films can then be deposited. It is necessary to add 1 x 10-4 Torr to 2 x 10-4 Torr of O2 gas during the deposition to maintain the stoichiometry of the film. The black titanium dioxide pieces are the more popular choice among our customers.
E-beam Evaporation of Titanium Dioxide (TiO2)
Titanium dioxide can be e-beam evaporated from a FABMATE® or tantalum crucible liner.
We recommend sweeping the e-beam at low power to uniformly melt the material and continue to add material to the crucible until an acceptable melt level is reached. Hole drilling should be avoided. Oxygen will be released during the pre-melt step and the material will become black. Pressure should be monitored to ensure outgassing is at an acceptable level before increasing power. If possible, Ion Assisted Deposition (IAD) and/or high substrate temperatures are preferred.
A partial pressure of O2 at 1-2 x 10-4 Torr is recommended. The evaporation temperature varies with composition. Titanium dioxide has a vapor pressure of 10-4 Torr at ~1,300°C. In our experience, we have been able to achieve a deposition rate of 3-5 angstroms per second.
Another key process note is to consider the fill volume in the e-beam application because we find that the melt level of a material in the crucible directly affects the success of the crucible liner. Overfilling the crucible will cause the material to spill over and create an electrical short between the liner and the hearth. The outcome is cracking in the crucible. This is the most common cause of crucible liner failure. Placing too little material in the crucible or evaporating too much material before refilling can be detrimental to the process as well. When the melt level is below 30%, the e-beam is likely to strike the bottom or walls of the crucible which immediately results in breakage. Our recommendation is to fill the crucible between 2/3 and 3/4 full to prevent these difficulties.
Crucible liners should be stored in a cool, dry place and always handled with gloves or forceps.
KJLC offers white and black titanium dioxide pieces. The difference in color is due to the material's degree of oxidation. Fully oxidized titanium dioxide is white. With even a slight reduction in oxygen, the material becomes grey to black in color. When evaporating titanium dioxide it is necessary to melt the material before depositing films. Titanium has several stable oxides, and when the material is heated it reduces (evolves oxygen) and turns black. Regardless of which material is used (white or black), the material will turn black and evolve oxygen as it is heated. Once outgassing subsides, the films can then be deposited. It is necessary to add 1 x 10-4 Torr to 2 x 10-4 Torr of O2 gas during the deposition to maintain the stoichiometry of the film. The black titanium dioxide pieces are the more popular choice among our customers.
See highlighted results that match your result in the table below.
Ordering Table
| More Info | Material | Description | Size | Quantity | Purity | Color | Part Number | Price | In Stock | Add To Cart |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| More Info | Material | Description | Size | Quantity | Purity | Color | Part Number | Price | In Stock | Add To Cart |
| Titanium Dioxide |
TITANIUM DIOXIDE PIECES, |
3mm - 6mm Pieces | 1 lb. | 99.9% | White to Gray | EVMTIO230 | P.O.R. |
|
||
| Titanium Dioxide |
TITANIUM DIOXIDE PIECES, |
3mm - 6mm Pieces | 50 g | 99.9% | White to Gray | EVMTIO230B | $92.00 |
|
||
| Titanium Dioxide |
TITANIUM DIOXIDE PIECES, |
3mm - 6mm Pieces | 100 g | 99.9% | White to Gray | EVMTIO230D | $160.00 |
|
||
| Titanium Dioxide |
TITANIUM DIOXIDE PIECES, |
3mm - 6mm Pieces | 1 kg | 99.9% | White to Gray | EVMTIO230KG | P.O.R. |
|