ConFlat® (CF) UHV Flanges & Components Technical Notes
ConFlat (CF) UHV Flanges
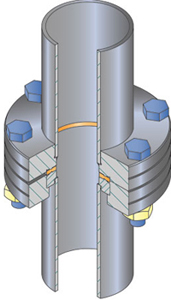
The CF flange (originally called ConFlat) is a sexless design where both flanges are identical. Typical flange materials are austenitic stainless steel types 304L, 316L, 316LN, and surface hardened aluminum (made from a weldable Al alloy). The seal mechanism is a knife-edge that is machined below the flange's flat surface. As the bolts of a flange-pair are tightened, the knife-edges make annular grooves on each side of a soft metal gasket. The extruded metal fills all the machining marks and surface defects in the flange, yielding a leak-tight seal (Figure 1). The CF seal operates from 760 Torr (1013 mbar) to < 1 x 10-13 Torr (<1.3 x 10-13 mbar), and within the temperature range -196° C to 450° C (depending on material). Flange sizes in North America (NA) are determined by outside diameter (O.D.). However, in Europe and much of Asia (E/A), the nominal internal diameter (nominal I.D.) of the largest tube that can be welded to a bored flange is usually referenced in their nomenclature.
The NA sizes are: 11/3" ("mini"), 23/4", 41/2", 6", 8", 10", 12", 131/4", 14" and 161/2" O.D.. The E/A sizes are digits (representing the nominal bore in mm) prefixed with either DN or NW (depending on manufacturer): DN16, DN40, DN63, DN100, DN160, DN200, and DN250. In addition, the NA system has intermediate O.D. sizes to enable the use of "standard" inch dimension tubes. They are 21/8" (1" diameter tube), 33/8" (2"), 45/8" (3"), 63/4" (5"). For other dimensions, see the ordering tables on this site.
CF flanges (with identical O.D.s up to 10" inclusive) from different (reputable) manufacturers will almost certainly seal.
The vacuum equipment industry adheres to the de-facto ConFlat standard.
ConFlat flanges are offered in four versions:
- Fixed flange (Figure 2): is a one piece design where the bolt-hole orientation is fixed with respect to that fitting.
- Rotatable flange (Figure 3): is comprised of two parts, an inner weld ring and outer bolt ring. This enables the bolt ring to rotate about the inner weld ring.
Both Fixed and Rotatable flanges are available with your choice of clearance-holes or tapped holes.
- Clearance-holes: Are through-holes that allow adequate clearance for bolts to go through both flanges and secured by nuts or plate nuts.
- Tapped holes: Are imperial or metric threaded holes machined through the flange. This allows a clearance-hole flange to be connected without the need for nuts or plate nuts. Be aware of a components bolt hole orientation when selecting tapped flanges.
Positive Pressures
When discussing system pressures, a common question is: What is the maximum internal pressure?
Positive pressures are inherently dangerous and failure comes without warning. In a vacuum system, failure depends on various strength properties of bolts, clamps, chamber walls, welds, feedthroughs, valves, viewports, etc. The only safe answer is that the internal absolute pressure cannot exceed the external absolute pressure.
ConFlat (CF) UHV Flange Gaskets
The gasket material sealing two flanges determines the joint's maximum temperature and, to an extent, the base pressure of the vacuum volume.
Metal gaskets are impermeable to gases and withstand moderately high temperatures indefinitely. The normal gaskets for stainless steel CF flanges are punched from 1/4 hard, high purity, oxygen-free (OFHC) copper stock. The gaskets are then chemically cleaned and processed to minimize scratches and burrs.
Bolting the flanges together causes the CF's knife-edges to deform the gasket. Under plastic flow, the copper fills in the knife-edges' imperfections and, in doing so, work-hardens—inducing the "springy" characteristics that keep the seal, even as the knife-edges are cycled from - 196° C to 450° C.
Given a correctly cleaned, baked, and pumped CF-flanged chamber, metal gaskets enable base pressures below 1 x 10-13 Torr (1.3 x 10-13 mbar). The work-hardening aspect means metal gaskets are one-time use only. There is strong anecdotal evidence that baking to 550° C for prolonged periods partially anneals the copper from its work-hardened state, since the joints will leak on cooling. When mounting fragile flanged components—e.g., viewports—fully annealed copper gaskets are recommended.
For systems requiring frequent high-temperature bakeouts, silver-plated copper gaskets are recommended. Without the plating, copper oxide forms on parts of the gasket exposed to air. It may flake into the chamber during flange disassembly.
Aluminum CF flanges must use aluminum gaskets — never copper. However, aluminum gaskets can be used on stainless steel CF flanges if baking is restricted to 200° C.
ConFlat (CF) UHV Flange Hardware
Regular nuts and bolts are not suitable for CF flange applications. Various high-tensile strength nut/bolt combinations made from low magnetic permeability, 18-8 stainless steel are used.
It is strongly recommended that all bolt, nut, platenut combinations are lubricated, either by one component being silver-plated or the application of a suitable thread lubricant.
Hex Head
Hex-head bolts (socket hex head for the mini flange) are long enough to penetrate two (through-hole) flanges and leave sufficient length for washers, nuts, or plate-nuts. For tapped and blind-tapped flanges, a shorter bolt length is used that does not penetrate the tapped flange or bottom out in a blind-tapped flange.
12-Point
Where high temperature bakeouts and frequent reassemblies are needed, (dry lubricated) 12-point cap screws are the best choice. Note that cap screws do not require special wrenches—the appropriate sized 12-point socket or flat wrench suffices.
Metric
Tapped metric flanges must use metric bolts. While through-hole flanges (built to metric specifications) will accept inch or metric nuts/bolts, it is strongly recommended that, for vacuum systems containing some tapped metric fittings, all nuts and bolts have metric threads.
Studs and Threaded Rods
This hardware is used to:
- Connect double-sided flanges
- Make bolts "emerge" from blind-tapped flanges
- Mount protective plastic covers over glass viewports
Both inch and metric threads are available for these and most other components.
Plate Nuts
These are metal plates with two threaded holes, shaped to match the corresponding CF flange's bolt hole patterns and replace the individual nuts (Figure 4). The plate nut's major advantage is, once two bolts are manually started, the plate nut acts as its own backing wrench and washer—the bolts are tightened using one wrench.